类
类的定义和使用
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age, gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
def show(self):
print(self.name)
# 实例化
person1 = Person('张三', 18, '男')
person2 = Person('李四', 20, '女')
person1.show() # 张三
person2.show() # 李四
类方法和静态方法
class A:
@classmethod
def print1(self):
print('print in class method')
@staticmethod
def print2():
print('print in static method')
A.print1() # print in class method
A.print2() # print in static method
接口和抽象类
由于 Python 没有抽象类、接口的概念,所以要实现这种功能得 abc.py 这个类库,具体使用如下:
接口
所有方法都必须在子类中实现。
import abc
class AInterface(metaclass=abc.ABCMeta):
@abc.abstractmethod
def func1(self): pass
class A(AInterface):
def func1(self): pass
a = A()
# 不实现则报错
# TypeError: Can't instantiate abstract class A with abstract methods func1
抽象类
部分方法在子类中实现。
import abc
class AInterface(metaclass=abc.ABCMeta):
@abc.abstractmethod
def func1(self): pass
def func2(self): pass
class A(AInterface):
def func1(self): pass
a = A()
a.func2()
# 不实现则报错
# TypeError: Can't instantiate abstract class A with abstract methods func1
三大特性
继承
单继承
class A:
def print(self):
print("print from A")
# B继承A
class B(A): pass
# C继承A
class C(A):
def print(self):
print('print from C')
b = B()
b.print() # print from A
c = C()
c.print() # print from C
当调用的方法在父类中已经存在同名方法,会默认调用子类的方法,如 C 类。如果子类中没有,则会调用父类的方法,如 B 类。
多继承
class A:
def print(self):
print('print from A')
class B:
def print(self):
print('print from B')
class C1(A, B): pass
class C2(B, A): pass
# C1类继承A类B类 C2类继承B类和A类
c1 = C1()
c1.print() # print from A
c2 = C2()
c2.print() # print from B
一个类继承多个类时,当调用的方法子类中没有时,会按继承顺序(从左到右)依次在父类中寻找并调用。
派生
子类拥有父类没有的方法或属性。
class A:
def print(self):
print('print from A')
class B(A):
def myprint(self):
print('print from B')
b = B()
b.print() # print from A
b.myprint() # print from B
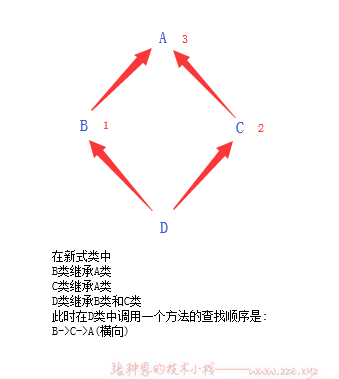
钻石继承及 super() 的执行顺序
class A:
def print(self):
print("print from A") # print from A 5
class B(A):
def print(self):
print('print from B') # print from B 1
print(super().print) # <bound method C.print of <__main__.D object at 0x00000000021EC6D8>> 2
super().print()
class C(A):
def print(self):
print('print from C') # print from C 3
print(super().print) # <bound method A.print of <__main__.D object at 0x00000000021EC6D8>> 4
super().print()
class D(B, C):
pass
d = D()
d.print()
# result:
# print from B
# <bound method C.print of <__main__.D object at 0x00000000021EC6D8>>
# print from C
# <bound method A.print of <__main__.D object at 0x00000000021EC6D8>>
# print from A
多态
Python 原生支持多态。
Java 中的多态
public interface Animal {
void talk();
}
public class Dog implements Animal{
@Override
public void talk() {
System.out.println("wangwang");
}
}
public class Pig implements Animal {
@Override
public void talk() {
System.out.println("aoao");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog();
dog.talk();
Animal pig = new Pig();
pig.talk();
}
}
Python 中的多态
import abc
class Animal(metaclass=abc.ABCMeta):
@abc.abstractmethod
def talk(self): pass
class Pig(Animal):
def talk(self):
print('aoao')
class Dog(Animal):
def talk(self):
print('wangwang')
dog = Dog()
dog.talk()
pig = Pig()
pig.talk()
封装
私有属性
属性或方法名前加双下划线声明私有属性或方法。对应 Java 中 private ,默认 public,无 protect(在类的外部仍然可以通过 实例._类名__属性名 调用)。
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age, gender, pwd):
self.name = name
self.__age = age
self.gender = gender
self.pwd = pwd
def __getpwd(self):
return self.pwd
person = Person('张三', 18, '男', '123')
print(person.name)
# print(person.__age) # AttributeError: 'Person' object has no attribute '__age'
print(person._Person__age) # 18
print(person.__getpwd()) # AttributeError: 'Person' object has no attribute '__getpwd'
封装属性
@property 可以将方法标识为一个属性。
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.__name = name
self.__age = age
@property
def name(self):
return self.__name
@name.setter
def name(self, new_name):
self.__name = new_name
@name.deleter
def name(self):
print('执行删除name操作')
p = Person('张三', 18)
print(p.name) # 张三
p.name = '李四'
print(p.name) # 李四
# 只是触发对应deleter装饰的函数,具体操作需在函数类完成
del p.name # 执行删除name操作
print(p.name) # 李四
-de8bd8f33c3e44a59907dafe1884f228.png)

评论区