准备环境
1、在前篇文章中的示例项目的基础上再引入 Redis 缓存的场景启动器:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、配置 Redis:
# application.yml
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: root
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.202.136:3306/springboot_cache
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
redis:
# 指定 redis 主机地址
host: 192.168.202.136
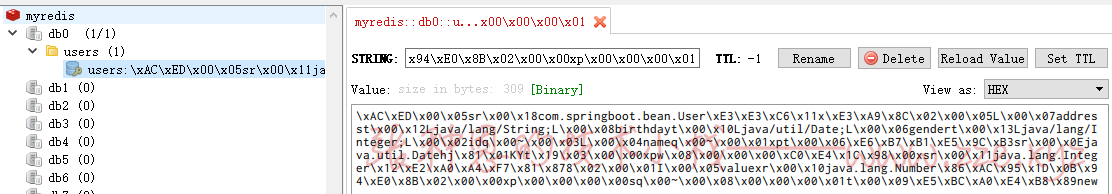
3、测试访问 localhost:8080/user/1,然后查看 Redis,会发现 id 为 1 的用户已经被缓存。
RedisTemplate 使用
import com.springboot.bean.User;
import com.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; // k-v 都为字符串
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; // k-v 都为 Object
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
// 操作字符串
@Test
public void testString(){
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("msg","hello 张三");
String msg = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg");
System.out.println(msg);
/*
hello 张三
*/
}
// 操作对象
// 注意:序列化类型需要实现 Serializable 接口
@Test
public void testObject(){
User user = userService.getById(2);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("id_2", user);
Object user2 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("id_2");
System.out.println(user2);
/*
User{id=2, name='李四', gender=0, birthday=Tue Feb 03 00:00:00 CST 1998, address='武汉'}
*/
}
/*
还可通过如下几种方式操作列表、集合、有序集合、哈希
RedisTemplate.opsForList()
RedisTemplate.opsForSet()
RedisTemplate.opsForZSet()
RedisTemplate.opsForHash()
*/
}
经过上述测试我们查看 redis 中数据会发现 redis 中保存的是 SpringBoot 以默认方式序列化后的数据,如果我们想要以 json 方式序列化保存数据到 redis 我们该怎么做呢?
我们使用的 RedisTemplate 和 StringRedisTemplate bean 都是在 redis 的自动配置类中注册的,查看:
// org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration.RedisConfiguration
@Configuration
protected static class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Object>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(StringRedisTemplate.class)
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
每个 RedisTemplate 对象都可定制自己的序列化器,查看源码会发现它默认使用的序列化器为 org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer。我们只需要修改它默认的序列化器即可:
// com.springboot.config.CacheConfig
import com.springboot.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, User> userRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
RedisTemplate<Object, User> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User> serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User>(User.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(serializer);
return template;
}
}
测试:
import com.springboot.bean.Dept;
import com.springboot.bean.User;
import com.springboot.service.DeptService;
import com.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTests {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate userRedisTemplate;
@Test
public void test(){
User user = userService.getById(2);
userRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("id_2", user);
Object user2 = userRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("id_2");
System.out.println(user2);
/*
User{id=2, name='李四', gender=0, birthday=Tue Feb 03 00:00:00 CST 1998, address='武汉'}
*/
}
}
自定义 CacheManager
上面说的是通过 RedisTemplate 操作保存 json 数据到 redis,如果要使用注解方式该怎么做呢?
一旦我们引入了 redis 缓存的场景启动器,那么默认生效的缓存配置类就变成了 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration :
// org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache;
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(RedisTemplate.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class)
@Conditional(CacheCondition.class)
class RedisCacheConfiguration {
private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;
private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker;
RedisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties,
CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker) {
this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties;
this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker;
}
// <1>
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate) {
// <2>
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true);
List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
}
return this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager);
}
}
缓存管理器也更换为 <1> 处的 RedisCacheManager,RedisCacheManager 帮我们创建 RedisCache 来作为缓存组件,而 RedisCache 组件就是通过操作 Redis 缓存数据的。
在 <2> 处也可以看到,创建 RedisCacheManager 实例时通过构造方法传入的 RedisTemplate,所以我们只需要自己定义一个 RedisCacheManager,让其 RedisTemplate 是使用 json 序列化器即可:
// com.springboot.config.CacheConfig
import com.springboot.bean.Dept;
import com.springboot.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, User> userRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
RedisTemplate<Object, User> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User> serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<User>(User.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(serializer);
return template;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Dept> deptRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
RedisTemplate<Object, Dept> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Dept> serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Dept>(Dept.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(serializer);
return template;
}
@Primary // 默认
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager userCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, User> redisTemplate) {
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
// key 使用 cacheName 作为前缀
cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true);
return cacheManager;
}
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Dept> redisTemplate) {
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
// key 使用 cacheName 作为前缀
cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true);
return cacheManager;
}
}
然后再使用注解时指定要使用的缓存管理器即可。
还可以通过手动编码方式获取到缓存管理器对指定缓存组件进行操作:
// com.springboot.service.DeptService
import com.springboot.bean.Dept;
import com.springboot.bean.User;
import com.springboot.mapper.DeptMappper;
import com.springboot.mapper.UserMappper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheManager = "deptCacheManager")
public class DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMappper deptMappper;
@Autowired
private RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager;
public Dept getById(Integer id) {
System.out.println("DeptService.getById(" + id + ") 执行了");
Dept dept = deptMappper.getById(id);
// 获取到缓存组件
Cache cache = deptCacheManager.getCache("dept");
cache.put(id, dept);
return dept;
}
}
-de8bd8f33c3e44a59907dafe1884f228.png)

评论区