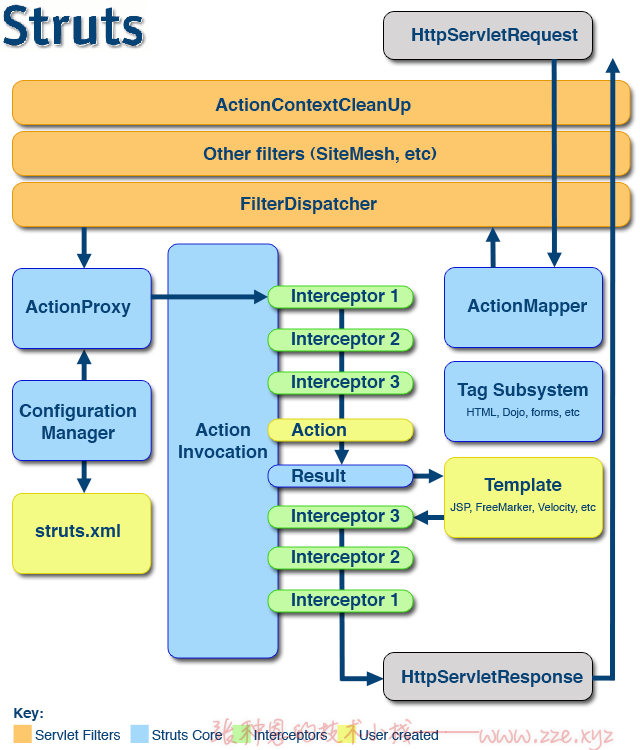
Struts2 架构图
源码分析
依旧是从核心过滤器的 doFilter 方法开始:
// org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter#doFilter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
// 判断当前请求 URL 是否在不处理范围内
if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
// 设置编码,默认 request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8")
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
// 创建 Action 及创建 ValueStack 值栈
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
// 将本次请求相关配置绑定到当前线程 ThreadLocal
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
// 包装原生 request ,对其进行增强
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
// 找到此次请求对应配置文件 struts.xml 中的映射相关信息,封装到 ActionMapping 实例
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) { // 未找到映射信息
// 查看此次请求目标是否是静态资源
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {// 找到了映射信息
// <1> 执行拦截器及 Action
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
// 清理请求信息
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}
进到 <1> 处的 execute.executeAction 方法:
// org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.ExecuteOperations#executeAction
public void executeAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, mapping);
}
继续进到 dispatcher.serviceAction 方法:
// org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.Dispatcher#serviceAction
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping)
throws ServletException {
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping);
// 从 request 中获取值栈
ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
boolean nullStack = stack == null;
if (nullStack) {
// 如果从 request 中未获取到值栈,则从 ActionContext 中取出值栈赋值给 stack
ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
stack = ctx.getValueStack();
}
}
if (stack != null) {
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack));
}
String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
// 创建 Action 代理对象
ActionProxy proxy = getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
// 将值栈放入 request
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
// <2> Action 代理开始执行过滤器和 Action
proxy.execute();
}
if (!nullStack) {
// 将已存在的值栈放入 Request
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
logConfigurationException(request, e);
sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (handleException || devMode) {
sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
} else {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
Action 及过滤器的执行在 <2> 处,查看 proxy.execute 方法:
// org.apache.struts2.impl.StrutsActionProxy#execute
public String execute() throws Exception {
ActionContext previous = ActionContext.getContext();
ActionContext.setContext(invocation.getInvocationContext());
try {
return invocation.invoke();
} finally {
if (cleanupContext)
ActionContext.setContext(previous);
}
}
在这里又执行 invocation.invoke 方法:
// com.opensymphony.xwork2.DefaultActionInvocation#invoke
public String invoke() throws Exception {
String profileKey = "invoke: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
if (executed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Action has already executed");
}
// <3> interceptors 是一个 Iterator (迭代器)对象,存放了所有拦截器的引用
if (interceptors.hasNext()) { // 如果存在下一个未迭代的拦截器
final InterceptorMapping interceptor = interceptors.next(); // 获取到拦截器
String interceptorMsg = "interceptor: " + interceptor.getName();
UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg);
try {
// <4> 执行拦截器的 intercept 方法
resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg);
}
} else { // 如果不存在下一个未迭代的拦截器
// 开始执行 Action
resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
}
if (!executed) {
if (preResultListeners != null) {
LOG.trace("Executing PreResultListeners for result [#0]", result);
for (Object preResultListener : preResultListeners) {
PreResultListener listener = (PreResultListener) preResultListener;
String _profileKey = "preResultListener: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(_profileKey);
listener.beforeResult(this, resultCode);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(_profileKey);
}
}
}
if (proxy.getExecuteResult()) {
executeResult();
}
executed = true;
}
return resultCode;
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
}
重点就在这个方法的 <3> 处的 if 判断块里了,这里在迭代所有拦截器,并且在 <4> 处把当前 DefaultActionInvocation 实例作为 invocation 参数传入执行了当前迭代的拦截器的 intercept 方法。而我们已经知道,拦截器中放行就是通过调用传入的 invocation 参数的 invocation.invoke 方法,即当前 invoke 方法。没错,这是一个递归!!!
Struts2 就是通过递归来迭代调用拦截器,这个递归能维持下去的条件有两个:
-
迭代器
interceptors中还存在未迭代的拦截器。 -
在迭代器的
intercept方法中必须调用invocation.invoke方法。
总结上述,Struts2 的执行流程如下:
- 客户端向服务器发送一个 Action 请求,首先执行核心过滤器 (
StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter) 的doFilter方法。 - 在这个方法中,调用了
ExecuteOperations实例execute的executeAction方法,而executeAction方法中又执行了Dispatcher实例dispatcher的serviceAction方法。 - 在
serviceAction中创建了Action代理对象proxy,这个代理对象为StrutsActionProxy的实例,接着执行了 Action 代理对象的execute方法。 - 在
execute方法中又执行了DefaultActionInvocation的实例invocation的invoke方法。 - 在
invoke方法中递归迭代执行拦截器,当拦截器迭代完毕,就会执行目标 Action 的目标方法,最后 Struts2 处理 Action 返回的逻辑视图结果,将处理结果交给response对象响应给浏览器。 - 通过上述代码也可以看到,Action 的执行时机是在迭代器正常执行完之后,到这里可以得出结论:
- 如果在迭代器中未调用
invocation.invoke,则后续的迭代器不会被执行,且 Action 也不会被执行,这就是invocation.invoke放行的原理。
-de8bd8f33c3e44a59907dafe1884f228.png)

评论区